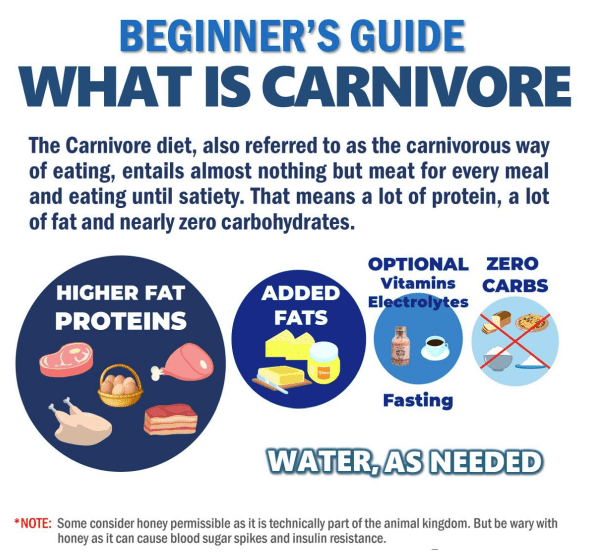
You may have heard of the carnivore diet, where individuals primarily consume meat-based foods while eliminating carbohydrates and plant-based foods from their meals. But did you know that there is a growing body of evidence suggesting a potential link between the carnivore diet and mental health? In this article, we will explore the fascinating connection between what we eat and how it may impact our mental well-being. Whether you’re curious about trying the carnivore diet or simply interested in understanding the impact of nutrition on mental health, this article will provide you with the essential information you need to know. So let’s dive in and discover how what you eat may have an unexpected influence on your mental state.
Introduction to the Carnivore Diet
The Carnivore Diet is a dietary approach that focuses on consuming only animal products, such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy, while completely eliminating plant-based foods. It is a highly restrictive diet that goes against the commonly recommended principles of eating a balanced and diverse diet. However, it has gained significant popularity in recent years, particularly within the fitness and wellness communities.
The basics of the carnivore diet
The carnivore diet is based on the principle that our ancestors primarily consumed animal products and that our bodies are better adapted to this type of diet. Advocates of the carnivore diet argue that it can lead to weight loss, increased energy levels, and improved overall health. By eliminating carbohydrates and plant-based foods, the diet aims to promote ketosis, a metabolic state where the body primarily uses ketones, derived from fat, as its main source of energy.
The rise in popularity
Although it may seem counterintuitive, the carnivore diet has gained a significant following in recent years. This can largely be attributed to the rise of social media and online communities, where individuals share their experiences and success stories. Popular figures within the fitness and wellness industry have also endorsed the carnivore diet, further contributing to its popularity.
The potential impact on mental health
While much of the focus around the carnivore diet has been on its impact on physical health, there is a growing interest in its potential effects on mental health. Emerging research suggests that there may be a link between diet and mental health, and the carnivore diet is no exception. Understanding this potential impact is essential for individuals considering adopting this type of diet and mental health professionals working with such individuals.
The Effect of Diet on Mental Health
The gut-brain connection
The gut-brain connection refers to the bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain. The gut is home to millions of bacteria, collectively known as the gut microbiota, which play a crucial role in regulating our physical and mental health. Emerging evidence suggests that the composition of the gut microbiota can influence brain function and mental health, potentially leading to improvements or exacerbation of mental health conditions.
The role of inflammation
Inflammation is a natural response by the body to protect against injury and infection. However, chronic inflammation has been linked to various physical and mental health conditions, including depression and anxiety. Diet plays a crucial role in modulating inflammation, and the carnivore diet, with its focus on animal products, may have an impact on inflammation levels in the body.
The impact of nutrient deficiencies
Adequate nutrient intake is essential for the proper functioning of the brain and the maintenance of mental health. Plant-based foods are rich in essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are important for brain health. By eliminating these foods, individuals following the carnivore diet may be at risk of nutrient deficiencies, which could potentially impact mental health.
Key Nutrients in the Carnivore Diet
Protein
Protein is an essential macronutrient that is necessary for the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues in the body. It plays a vital role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and serotonin, which are involved in regulating mood and mental health. The carnivore diet, with its emphasis on animal products, provides ample amounts of high-quality protein.
Fatty acids
Fatty acids, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, are crucial for brain health and the prevention of mental health conditions. They play a role in the development and maintenance of brain cells, as well as the regulation of neurotransmitter function. While the carnivore diet may be rich in certain types of fatty acids, such as those found in fatty fish, it may be lacking in other types, such as omega-3 fatty acids from plant-based sources.
Vitamins and minerals
Vitamins and minerals are essential micronutrients that are crucial for brain function and mental health. Plant-based foods are typically rich in vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, folate, and magnesium, which have been linked to improved mental health. The carnivore diet may be lacking in these nutrients unless individuals carefully select a wide variety of animal products.
Effects of the Carnivore Diet on Mental Health
Improvement in mood and depression
Some individuals following the carnivore diet have reported improvements in their mood and a reduction in symptoms of depression. While the underlying mechanisms are not yet fully understood, it is believed that the elimination of potential trigger foods, such as processed carbohydrates and certain plant compounds, may play a role in these improvements.
Reduction of anxiety symptoms
Anecdotal evidence suggests that the carnivore diet may also lead to a reduction in anxiety symptoms. This could be attributed to the elimination of potential allergens or inflammatory foods, as well as the impact of high-quality protein and fats on neurotransmitter function.
Regulation of dopamine levels
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in reward and pleasure pathways in the brain. Imbalances in dopamine levels have been implicated in mental health conditions such as depression and addiction. The carnivore diet, with its focus on protein-rich animal products, may help regulate dopamine levels and improve overall mental well-being.
Contradictory Findings and Controversies
Conflicting studies on the carnivore diet and mental health
While there is limited research specifically examining the carnivore diet’s impact on mental health, some studies have produced contradictory findings. This highlights the need for more controlled studies to better understand the potential effects of this dietary approach on mental health.
Consideration of individual variability
It is important to consider that each individual is unique and may respond differently to the carnivore diet. What works for one person may not work for another, and factors such as genetics, gut microbiota composition, and pre-existing mental health conditions may influence the outcomes.
The role of other lifestyle factors
Diet is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to mental health. Other lifestyle factors, such as physical activity, sleep, stress management, and social connections, also play a significant role. It is important to consider these factors holistically when evaluating the potential benefits or risks of the carnivore diet.
Potential Mechanisms Behind the Benefits
Elimination of potential trigger foods
By eliminating certain foods, such as processed carbohydrates and plant compounds, that may contribute to inflammation or trigger allergies or sensitivities, the carnivore diet may provide relief for individuals with mental health conditions. However, further research is needed to understand the specific mechanisms underlying these benefits.
Optimization of nutrient intake
The carnivore diet, when followed with careful consideration and variety, can provide adequate amounts of essential nutrients such as protein, fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals necessary for optimal brain health and mental well-being. This optimized nutrient intake may contribute to the reported improvements in mental health on the carnivore diet.
Reduced inflammation and oxidative stress
The carnivore diet, with its potential to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, may have a positive impact on mental health. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress have been linked to the development and progression of mental health conditions, and by addressing these underlying factors, the carnivore diet may offer some relief.
Case Studies and Personal Experiences
Anecdotal evidence of mental health improvements
Many individuals following the carnivore diet have reported significant improvements in their mental health, including reductions in symptoms of depression, anxiety, and mood disorders. While anecdotal evidence should be interpreted with caution, the sheer number of positive testimonials warrants further investigation into the potential benefits.
Success stories and reported benefits
Numerous success stories have emerged from individuals who have experienced transformative mental health improvements on the carnivore diet. These stories often highlight improvements in mood, energy levels, focus, and clarity. However, it is important to note that individual experiences may vary.
Discussion of self-reported observations
Online communities have become a platform for individuals to share their self-reported observations and experiences with the carnivore diet and mental health. While these observations may provide valuable insights, they should be considered as preliminary evidence and not as definitive scientific findings.
Hurdles and Risks of the Carnivore Diet
Challenges in maintaining a well-rounded diet
The carnivore diet’s restrictive nature poses challenges in obtaining a well-rounded and balanced intake of essential nutrients. It requires careful planning and supplementation to ensure adequate nutrient intake, which may be difficult for some individuals to maintain in the long term.
Potential nutritional deficiencies
By eliminating plant-based foods, individuals following the carnivore diet may be at risk of certain nutritional deficiencies, such as vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants. These deficiencies could have adverse effects on mental health and overall well-being.
The controversy surrounding long-term sustainability
The long-term sustainability of the carnivore diet is a topic of debate among experts. While anecdotal evidence suggests that some individuals thrive on this dietary approach, there are concerns about potential health risks associated with long-term exclusion of plant-based foods and the lack of long-term scientific research.
Considerations for Mental Health Professionals
Assessing the appropriateness of the carnivore diet for clients
Mental health professionals should carefully assess the appropriateness of the carnivore diet for their clients. Factors to consider include individual health history, pre-existing mental health conditions, nutrient intake requirements, and the client’s ability to adhere to the diet in a healthy and sustainable manner.
Educating clients about potential risks and benefits
It is essential for mental health professionals to educate their clients about the potential risks and benefits associated with the carnivore diet. They should provide evidence-based information and support clients in making informed decisions about their dietary choices, while ensuring their overall mental and physical well-being.
Incorporating dietary changes into treatment plans
For clients who choose to follow the carnivore diet, mental health professionals can incorporate dietary changes into their treatment plans. This may involve collaborating with registered dietitians or nutritionists to ensure adequate nutrient intake, monitoring for potential nutritional deficiencies, and regularly assessing the client’s mental health and well-being.
Future Research and Recommendations
The need for more controlled studies
To better understand the potential effects of the carnivore diet on mental health, more controlled studies are needed. This would involve comparing the mental health outcomes of individuals who follow the carnivore diet to those who follow other dietary approaches or a more balanced and diverse diet.
Exploration of the long-term effects
Long-term studies are crucial to assess the safety and sustainability of the carnivore diet. This would involve monitoring individuals over an extended period to evaluate the potential risks, including potential nutrient deficiencies and the impact on mental health in the long run.
Tailoring the carnivore diet for mental health conditions
Further research is needed to explore the potential benefits of tailoring the carnivore diet for individuals with specific mental health conditions. For example, evaluating the impact of the diet on individuals with depression, anxiety disorders, or neurodevelopmental disorders such as ADHD could provide valuable insights into its potential therapeutic role.